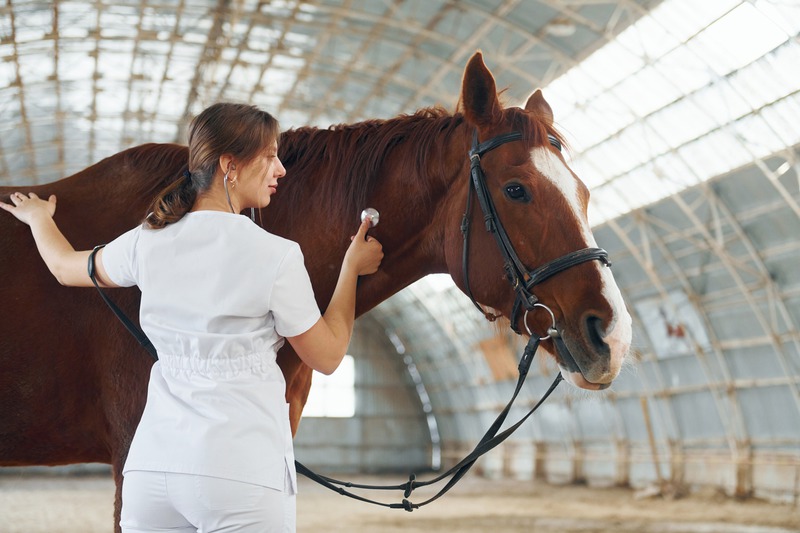
If you’re a horse owner, you know that keeping your equine friend happy and healthy is a top priority. One of the problems that can dampen the spirit of these majestic animals is lameness. It’s a troublesome condition that can arise from various causes, and understanding them is key to prevention and treatment. In our chat today, we’re going to unpack the common reasons behind horse lameness, giving you the insights you need to ensure your hoofed companion stays in tip-top shape.
Horse Anatomy and Lameness
Before we delve into the causes of lameness, it’s essential to appreciate the complexity of a horse’s anatomy. Their legs – a major marvel of evolutionary design – carry substantial weight and are subject to immense stress, whether through daily activities or during intense performance. Lameness typically signifies that there’s something amiss within this intricate system of bones, tendons, ligaments, and hooves, causing discomfort or pain to the animal.
Common Culprits Behind Lameness
Hoof Issues
Let’s start from the ground up – the hoof. This part of the horse is often where trouble begins. Common hoof problems include:
-
Abscesses: These are painful pockets of pus that develop within the hoof, usually caused by bacteria entering the hoof through a small crack or wound.
-
Bruises: Just like humans, horses can bruise, too. Hoof bruises are often the result of stepping on a hard object or repetitive stress on the hoof.
-
Laminitis: This serious condition involves inflammation of the laminae, the tissues that attach the hoof to the foot’s bone, and can lead to severe lameness.
Joint and Bone Issues
Moving up from the hoof, we come to the bones and joints, which are also common sites of lameness:
-
Arthritis: Just like in humans, horses can suffer from joint pain due to arthritis, especially as they age.
-
Fractures: Bone breaks can occur from trauma or stress and can range from minor to serious.
-
Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD): This condition involves the cartilage in the joints and can lead to lameness, especially in younger, growing horses.
Tendon and Ligament Injuries
Strains and sprains aren’t exclusive to human athletes – horses get them too. Injuries to tendons and ligaments are a significant cause of lameness and include:
-
Tendonitis: An inflammation or injury to a tendon, often seen in racehorses and performance horses.
-
Suspensory ligament injuries: These crucial ligaments support the horse’s leg during weight-bearing and can become damaged through overuse or accident.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammation due to various diseases or infections can also lead to lameness. These conditions might include:
-
Synovitis: An inflammation of the joint lining that can cause swelling and pain.
-
Septic arthritis: Caused by a bacterial or fungal infection within a joint, leading to a painful, swollen, and hot joint.
Emergency Situations and Immediate Care
Sometimes, lameness can be an emergency – particularly if it’s due to a severe injury or a sudden onset of pain. In these instances, knowing an emergency horse vet in Ocala can be a lifesaver. Immediate care might involve administering pain relief, stabilizing a fracture, or other urgent interventions to keep the horse comfortable before it can receive specialized treatment.
Spotting the Signs of Lameness
Detecting lameness involves observing changes in your horse’s gait, behavior, or willingness to move. Signs to look for include:
-
Uneven weight bearing or limping
-
Difficulty in turning or reluctance to canter
-
Swelling or heat in the limbs
-
Changes in behavior or mood, which might signal discomfort
When to Seek Veterinary Help
Whenever you suspect your horse might be lame, it’s essential to consult a professional. Take your time, as early intervention can make a huge difference in the outcome. A treatment for lame horse in Ocala might include a variety of approaches, depending on the cause of lameness. Treatment options such as rest, medication, shoeing changes, or surgery can be tailored to your horse’s specific needs by a skilled veterinarian.
Preventive Measures and Management
To minimize the risk of lameness, several management strategies can be helpful:
-
Regular hoof care and shoeing by a qualified farrier
-
Proper nutrition to maintain healthy bones and joints
-
Adequate exercise and avoidance of overtraining
-
Immediate attention to any signs of pain or injury
Transporting an Injured Horse
If you’re faced with a situation where your horse cannot walk due to severe lameness, utilizing an equine ambulance could be necessary. These specialized vehicles are equipped to safely transport injured horses, providing them with the support and care they need en route to a veterinary facility.
Final Thoughts
Today, we talked about the various reasons horses can become lame, including problems with their hooves, joints, bones, and soft tissues, as well as inflammation. It’s important to notice any signs of lameness quickly and consult a vet right away. Knowing emergency options also helps protect your horse’s health. Always aim to prevent issues before they happen by taking good care of your horse helping it to remain healthy and active.